

In my earlier video I explained the concept of Threat analysis and the STRIDE threat classification scheme. In that video I looked at the theory, but in this video I explain how it can be used in a real example using an Internet of Things (IoT) project using a Raspberry Pi computer.
This is simplified but should help show how you turn the theory into practice.
Transcript: Cybersecurity STRIDE analysis of a Raspberry Pi IoT project - Video Transcript
This is also one of the key learning points in CISSP section 1.
The example project used is my Raspberry Pi Pixel Server.This IoT project started life as a non-secure application designed for use on a secure network, but as I wanted to make it suitable for connecting to the Internet I decided I needed to implement the CIA triad and the AAA security framework. This also meant that I should perform cybersecurity threat analysis to ensure that the application is secure before connecting it to the Internet.
![]()
The 6 steps to STRIDE are:
Below are the data flow diagrams that I used. These are to focus on just two aspects, the network connectivity and the internal storage of usernames.
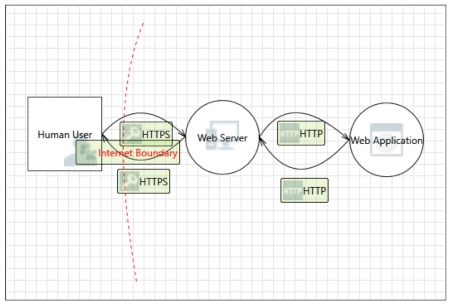
This diagram is based on the network data flows. The central part is a web server, which is an nginx web server. In this instance it's primarily acting as a reverse proxy adding SSL/TLS encryption to data being passed over the Internet. The requests from the user arrive as https to the reverse proxy, which are then passed to the web application (Python Flask web app) as http. The web application responds back to the reverse proxy, which sends the response back to the human user as encrypted SSL/TLS HTTPS.
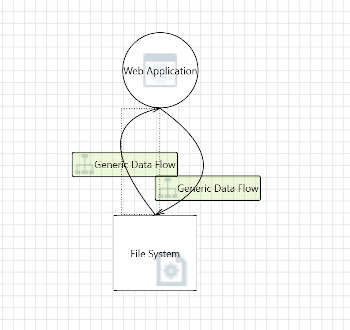
This diagram shows the local data flow between the web application and the local file system which is used to store the hashed user passwords.
Based on the above diagrams I performed STRIDE threat analysis by looking for threats against each of the 6 STRIDE categories.
Analysis was performed using the Microsoft Threat Analysis Tool, but also using manual means looking at possible threats where data flows from one component to another.
Some of the threats identified are listed below.
The next step is to assess those threats, prioritize and respond to the threats. This is used to identify and allocate resources to mitigating the threats. There are different ways that the risk can be assessed such as probability vs damage; high / medium / low risk; a heatmap or the DREAD system.
Based on this I identified the following four as the main threats to address (this is only a partial list, some of the other threats had already been addressed and others were considered at a later stage):
As a summary the STRIDE threat analysis has provided a way to identify risks and work out steps to mitigate the risks. There are other threat analysis methodologies that can be used, but this is useful for identifying threats that could otherwise be missed.
This analysis can be performed using the Microsoft Threat Analysis Tool or manually.
Please subscribe to Penguin Fortress on YouTube for future videos.
For more details about how security see the following guides: